What is Obesity?
Obesity is a medical condition where there is increased buildup of body fat to the extent that it may have a negative effect on health. It is normally defined using the Body Mass Index (BMI), which is based on your weight and height.
Why does Obesity Matter?
Obesity can lead to many health problems, including but not limited to:
- Heart Disease and Stroke: Excess fat can cause increased blood pressure, high cholesterol, and can lead to clogged arteries, all of which increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes, as it affects the way the body processes blood sugar.
- Sleep Apnea: Excess weight can affect breathing and lead to sleep apnea and other breathing issues.
- Fatty Liver Disease: This condition, which involves the buildup of fat in the liver, can lead to liver damage.
- Mental Health Issues: Obesity can impact mental health, leading to issues such as depression, anxiety, and lower self-esteem.
What Can I Do to Lose Weight?
- Diet: A balanced diet can include fruits, vegetables, whole grains and healthy fats, while also avoiding food with saturated and trans-fats.
- The Mental Battle: The journey to weight loss is also a mental one. Recognizing emotional challenges and building a support system is vital.
- Increased Physical Activity: 300 minutes a week or more of activity that makes your heart work a little harder may help with weight loss or keeping off lost weight
- Medications: Medications are available that can help diet and exercise for those struggling with obesity when lifestyle changes alone are not enough.
What Medications Can Help with Weight Loss?
Short-Term Medications
Temporary medicines used for losing weight mostly work by increasing metabolism and may make you feel less hungry. They change the way some brain chemicals work to help you feel full. These medicines can sometimes cause increased blood pressure and heart rate or be misused, so FDA recommendations are to only use these medications for 3 months or less. Here are some of the usual ones people take to lose weight:
- Adipex-P (phentermine)
- Benzphetamine
- Phendimetrazine
- Diethylpropion
Long-Term Medications
Long term medications are available that can help diet and exercise for those struggling with obesity, particularly when lifestyle changes alone are not enough. Common medications work by reducing appetite, increasing feelings of fullness, or decreasing the absorption of fat.
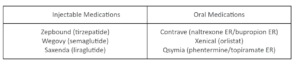
While these medications can be effective, they also come with potential side effects. Always talk to your doctor before starting any medication. They can provide the best advice based on your health profile.
How Do These Newer Medications Work?
Saxenda, also known as liraglutide, was the first of its kind for weight loss. People take it once a week via injection, and it can help them lose around 14 pounds. Wegovy, also known as semaglutide, is newer and might help people lose more weight, about 34 pounds on average. They work by making you feel full, so you eat less. Both are used with diet and exercise. Common side effects include stomach issues, but serious problems are rare.
Zepbound is a newer type of weight loss medicine, known also as tirzepatide. It’s like Wegovy and Saxenda, but it also works to help your body handle sugar and energy. You take it once a week via injection, and it can help you lose even more weight. In studies, people lost about 28 pounds with Zepbound, diet, and exercise. Side effects are similar, including stomach issues.
How Long Do I Need to Take These Medications?
If you stop taking Zepbound (tirzepatide) or similar medications like GLP-1 agonists, you are likely to regain a large portion of the weight you lost while on the medication. Because of the difficulties many people face in keeping weight loss, lifelong treatment may be needed. Talk to your doctor about what medication and duration would best fit your needs.
References:
- Zepbound [package insert]. Indianapolis,IN: Eli Lilly; 2023.
- Muniraj T, Day LW, Teigen LM, Ho EY, Sultan S, Davitkov P, Shah R, Murad MH. AGA Clinical Practice Guidelines on Intragastric Balloons in the Management of Obesity. Gastroenterology. 2021 Apr;160(5):1799-1808. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.03.003. PMID: 33832655.
Written by:
Pritesh Patel
Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate 2024
Philadelphia College of Pharmacy
